Is the Bitcoin network secure? Why do you hear about hackers stealing Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies? Is Bitcoin only used by criminals? Can I trust Bitcoin more than my trusted credit card? The answer to these questions and more as we dive into the security of Bitcoin for the average investor.
What is Cryptography?
In order to grasp a basic understanding of how Bitcoin is an extremely secure network, you need to know a little about cryptography. Cryptography is the field of work underlying the technology behind Bitcoin.
The word cryptography itself essentially means, the study of “solving hidden codes.” Hidden codes have been used for centuries to encode secret messages on the battlefield or hide messages from your rivals as far back as 1900BC. As a modern-day academic field of research, Cryptography expands into the world of mathematics, computer science, electrical engineering, physics, and communications.*
Bitcoin uses the science of cryptography to secure and communicate digital values. Just like a general in the army sending an encrypted message to the troops on a battlefield so Bitcoin uses encryption to secure transactions on the network. The only difference is instead of the communication containing a verbal message, the Bitcoin network carries transactions that contain money.
For the purposes of this blog, and my desire to communicate to the average investor, I’m not going to get into the complexities of how transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain work (plus it is super complicated and I’d probably butcher it).
It will suffice to say that Bitcoin transactions use mathematical functions that are easy to calculate in one direction but are mathematically impossible to calculate in the opposite direction. This creates a beautiful mix of security and transparency.
Each Bitcoin account (or wallet) makes use of a private key and a public key that allows for the secure storage of funds and transparent sending of funds. For those who want to dive deep into this, Bitcoin uses elliptic curve multiplication (yep, google that if you’re feeling really wild one day) and cryptographic hash functions to facilitate transactions.* Please read Mastering Bitcoin, by Andreas Antonopolous if you’d like to learn more about the way this works.
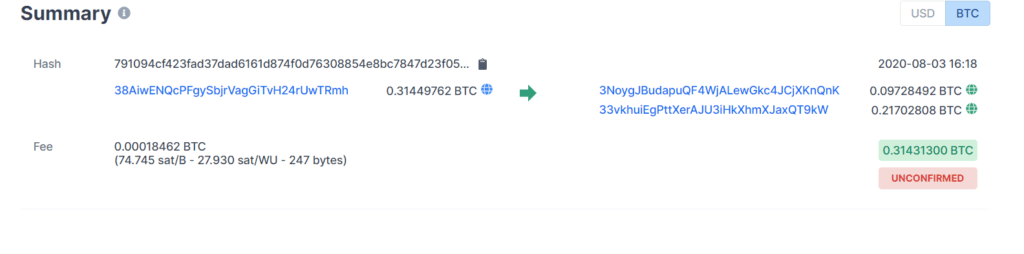
Summary of how Bitcoin uses Cryptography in one transactions simple enough for anyone to understand:
- Bitcoin transactions are transparent. Anyone can see which wallet is sending bitcoin from one wallet to another.
- The amount of Bitcoin in each transaction and the total Bitcoin in each wallet is public information.
- However, the identity of who holds each wallet is private.
- Only the owner of a Bitcoin wallet has access to the funds.
Like using cash, your identity when using Bitcoin is mostly autonomous. I like the word pseudo-anonymous
Cryptography and the Blockchain
Every Bitcoin transaction is recorded in a block. Essentially, a block is a grouping of transactions that occurs roughly every ten minutes. When people talk about the “blockchain,” a massively popular buzz word in the world of finance right now, all they are talking about is this online digital ledger of transactions.
If you use a Visa card to buy something online at Amazon. Amazon communicates with Visa to verify that this transaction happened. If someone steals your credit card data, they may be able to make some purchases and buy some stuff on your tab. With credit card transactions, a buyer submits all of his or her private information to the seller in hopes that that information is not compromised. We have all seen massive amounts of private consumer information taken by fraudsters in recent years. In 2019, Captial one exposed the private information of over 106 million customers.*
With Bitcoin, every transaction is processed without verification from a third party. Once a transaction occurs, it is sent to an online system of “miners” whose function is to verify that each transaction occurred and that both parties digitally agree on the transaction.
The only people directly involved in the transaction are the buyer and the seller. There is no potential for a chargeback or fraud. The transaction can only be refunded by the seller.
Each block contains a group of transactions and is irreversibly tied to the previous block. When a transaction occurs, it is confirmed by the entire network of Bitcoin miners and nodes to ensure its integrity. Bitcoin miners are spread throughout the world in various places and are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoin for their efforts. The miners are incentivized to keep the system honest. Because each block is irreversibly linked to the last, every transaction that ever took place on the Bitcoin network is etched into the history of the time and verified by miners around the world (decentralized).
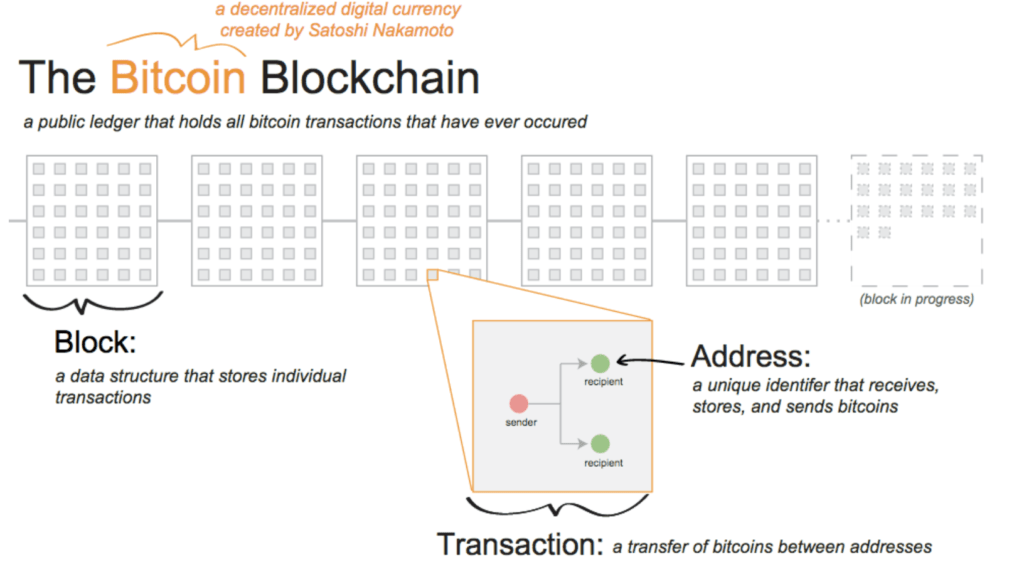
With Bitcoin, a user doesn’t need to trust a third party with their data. If someone were to decide they wanted to pass fraudulent transactions on the network they would have to control more than 50% of the network’s computing power dedicated to mining and verifying transactions. Even then, this heist would be extraordinarily expensive and shortlived.
When it comes to SECURITY Bitcoin beats Credit Cards any day of the week.
Fraud – Bitcoin Fixes This
Identity Theft – Bitcoin Fixes This
PCI Compliance – Bitcoin Fixes This
Charge-backs and Fees- Bitcoin Fixes This
Bitcoin Encryption
Bitcoin uses what is called SHA256 bit encryption. This is a fancy term to basically say that it cannot be hacked. Imagine trying to guess a four-digit pin code. You could guess 0000, 0001, 0002, and so on until you found the answer. SHA256 bit encryption is basically saying that in order to guess a code you would need to guess every combination of a 256-bit number. The total number of 256-bit numbers is 2256. This is an extraordinarily massive number.
Bitcoin uses encryption when both creating the private keys that protect your Bitcoin wallet and on the blockchain to validate each block. To give you an idea of how strong this encryption is experts estimate that it would take a supercomputer that can perform 15 trillion calculations per second .65 billion- billion years to crack one line of 256-bit encryption.* That second billion is not a typo. This article from Hackernoon goes on to explain even a Quantum computer (which does yet exist) would likely take over the 10^ ³² years, which is longer than the universe has been in existence.
Feel rest assured, the technology and mathematics behind Bitcoin ensures the system is more than secure.
Isn’t Bitcoin just for Criminals?
A common theme floated around by the mainstream media is that Bitcoin is only used by criminals. In January 2020, The New York Times released a piece entitled, “Bitcoin is losing steam, but criminals still love it.”* In the early days of Bitcoin many criminals did use it on the dark web to purchase illegal items on websites like Silk Road.
The truth is that the most recent data suggests that only 1% of Bitcoin transactions in 2018 were used for illegal purposes.* As criminals have become more knowledgable in Bitcoin, they have found that it isn’t the best currency to conduct illegal business with.
As pointed out above, all Bitcoin transactions are transparent. Newly formed law enforcement agencies are actually fans of criminals that use Bitcoin because the Bitcoin Blockchain leaves an immutable ledger of all transactions. Anyone can pull up a history of transactions and “follow the money” to help investigators identify the wallets used by the perpetrators and stop further activities.
Since Bitcoin is only semi-anonymous this makes hackers, illegal websites, and other wrongdoers using the currency a little more cautious about their activities. Clever thieves have found ways of laundering Bitcoin by sending their coins to mixer services that essentially create multiple addresses and distribute funds making it harder to track. However, governments have been cracking down on these mixing services and finding better means of forensic investigations on blockchains.
Companies like Price Water House Coopers, Merkle Science, Chainanalysis, and Elliptic have developed powerful blockchain forensics tools to help catch bad actors and illicit activities. Following large exchange hacks, that involve millions of dollars worth of stolen cryptocurrency these tools have helped identify the wallets used by the criminals. These addresses have been blacklisted by many major exchanges to ensure these stolen coins can’t be used in the future.
The bottom line is while Bitcoin can be used by criminals, it is far from an ideal currency to use if you wish to break the law.
Can Hackers Hack Bitcoin?

The decentralized nature of Bitcoin renders the network virtually unhackable. However, this does not mean that Bitcoin is completely invulnerable to attacks. The way individuals and companies hold Bitcoin is what makes it vulnerable to attacks, not the Bitcoin network itself.
Hackers have frequently targeted cryptocurrency exchanges as they hold massive amounts of coins (not just Bitcoin). Using malware, phishing techniques, and other traditional hacking techniques, unscrupulous individuals are able to gain access to the back-end files of the exchange. This is where the trouble happens. Most exchanges hold their funds in “hot wallets”, which are connected to the internet at all times. Like any bank or secure site, customers need to be able to interact with their funds through passwords and other forms of authentication. If hackers are able to gain access to saved customer information they can access the private keys to their cryptocurrency.
In short, the Bitcoin network is next to impossible to hack, but holding your coins in online wallets leaves you susceptible to attacks. With the proper Bitcoin storage and the use of trusted websites, holding cryptocurrency can be a very secure practice. Savvy Bitcoin investors and custody companies take time and effort to hold their Bitcoin keys in offline wallets called cold wallets. Reputable exchanges use a variety of offline and online wallets to ensure even if they are hacked the damage is minimal. It rests on both exchanges and individuals to educate take the precautions necessary to protect their investments. In a future article, I will be explaining the best ways to store your Bitcoin.
Summary
The technology behind Bitcoin makes it extraordinarily secure. However, individuals need to the necessary precautions in how they secure their wallets. Many of the security concerns you hear about Bitcoin are myths often propagated by those who either don’t understand or are afraid of Bitcoin. Happy investing!
Please read our disclaimer here regarding investment advice and risk. Disclaimer: This should not be construed as or relied upon in any manner as investment, legal, tax, or other advice. Please consult an appropriate tax or financial professional to understand your personal tax and financial circumstances. I may get compensated by some platforms mentioned below (because of referral links). Do your own research.
*https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptography
*Mastering Bitcoin: Unlocking Digital Currencies – Andreas Antonopoulos
*https://www.investopedia.com/news/5-biggest-credit-card-data-hacks-history/
*https://hackernoon.com/a-physicists-journey-into-cracking-bitcoin-4631e57158cc
*https://www.nytimes.com/2020/01/28/technology/bitcoin-black-market.html

